- You are here:
- Home
- Incoterms: International Commercial Terms
Incoterms: International Commercial Terms
What are they?
Created in 1936 by the International Chamber of Commerce, Incoterms (short for International Commercial Terms) are a set of rules that define who is responsible for different tasks during international transactions.
In addition to being a requirement on commercial invoices, Incoterms significantly reduce the risk of costly misunderstandings. They, thus, cover everything concerning costs, tasks and risks associated with the transaction of goods between seller and buyer.
In fact, Incoterms are clauses intended to avoid disputes. These rules only apply to exporters and importers and do not apply to carriers, insurers and shippers.
The choice of Incoterm is inherent to commercial negotiations, so one must take into account the organizational capacity of the company, the means of transport used and the service to be provided.
Objectives
Incoterms serve three major purposes:
- Set up cost transfer
- Define risk transmission
- Define the location from which the goods depart
The seller must include the expenses of the sales contract in the price. This way, the buyer knows which expenses must be added to the purchase price and can compare them with other offers.
The Incoterms define the time and place from which the seller's responsibility ends and the buyer's begins.
The Incoterms indicate the place where the seller must deposit the goods and, therefore, the place where the buyer will pick them up.
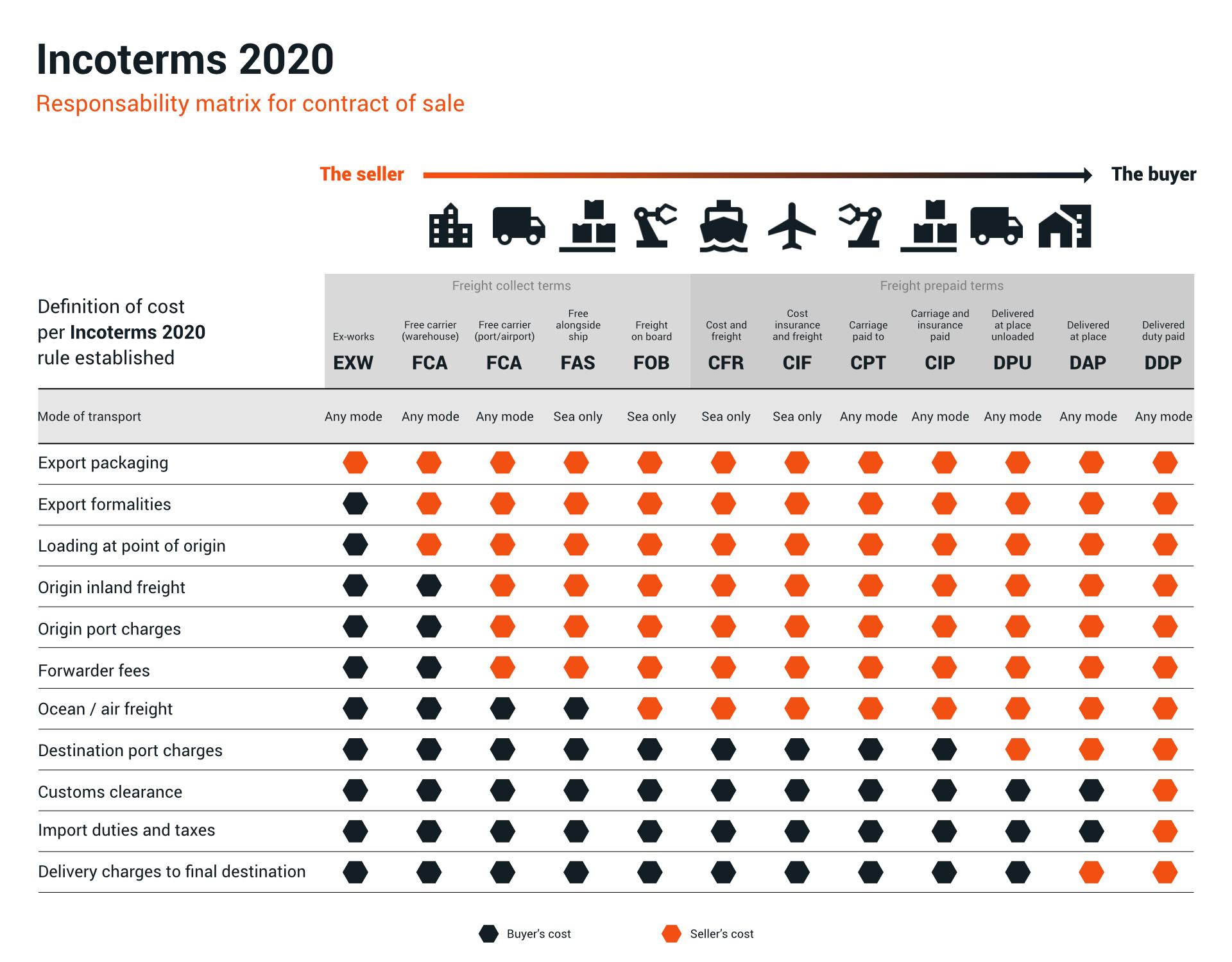
What are the Incoterms
Usually, Incoterms are represented by three-letter acronyms.
The buyer is responsible for most of the costs and risks associated with the shipping process. So, the seller only has to make sure that the buyer can access the products. Once this happens, the rest is entirely the responsibility of the buyer.
The seller covers the risks and costs associated with transporting the goods to a stipulated address. The goods are considered to be delivered as soon as they arrive at the address and can be unloaded. Responsibility ceases to be the seller's when the goods are placed at the buyer's disposal.
The seller assumes almost all responsibility during the shipping process, charging all costs and risks associated with transporting the goods to the agreed address. The seller has to pay all fees, has to confirm that the goods are ready to be unloaded and that export and import regulations are followed.
The seller pays for transportation of the goods and insurance to the agreed destination. In addition, it is obliged to purchase the maximum level of cover indicated in Clause A of the Institute Cargo Clauses.
The seller is responsible for the costs and risks associated with delivering the goods to a pre-arranged unloading point. The seller must also leave the goods at the unloading point. The buyer, in turn, arranges for import clearance and associated fees.
The seller must ship the goods to the buyer's carrier at the agreed location. In addition, the seller must clear the goods for export.
The seller must ship the goods to the buyer's carrier at the agreed location and must cover all delivery costs. It is also the seller's duty to clear the goods for export.
The seller bears all costs and risks until the goods are delivered to the ship. After that, the responsibility lies with the buyer, who must handle the import and export formalities.
The seller assumes all risks and costs until the goods are delivered on board the ship. Besides, he takes care of the export formalities. The buyer, on the other hand, assumes all these responsibilities once the goods are on board.
Besides assuming all risks and costs until the goods are delivered on board the ship, the seller has to pay the cost of transporting the goods to the port. The buyer, on the other hand, assumes all responsibilities once the goods are on board.
Assuming all risks and costs until the goods are delivered on board the ship, the seller must pay the cost of transportation to the port as well as the cost of insurance. The seller is also required to purchase the minimum insurance coverage, which concerns 110% of the invoice value. If the buyer needs more comprehensive insurance, the seller arranges for the additional coverage, with the buyer bearing this cost.
Contact Us
Need to know more informations about this solution? That's the reason we are here for.
If you have questions and are interested about this solution, don't be afraid to ask. We have a comercial team ready to answer your questions!



